-
[Airflow] - Concept개발/Airflow 2022. 8. 3. 15:40
Airflow Default Concept
1. Operator
An Operator is conceptually a template for a predefined Task, that you can just define declaratively inside your DAG
For a list of all core operators(built-in)
- BashOperator - executes a bash command
- PythonOperator - calls an arbitrary Python function
- EmailOperator - sends an email
with DAG("my-dag") as dag: ping = SimpleHttpOperator(endpoint="http://example.com/update/") email = EmailOperator(to="admin@example.com", subject="Update complete")Jinja Template
Airflow leverages the power of Jinja Templating and this can be a powerful tool to use in combination with
macros#BashOperator Example # The start of the data interval as YYYY-MM-DD date = "{{ ds }}" t = BashOperator( task_id="test_env", bash_command="/tmp/test.sh ", dag=dag, env={"DATA_INTERVAL_START": date}, )- {{ ds }} is a templated variable.
- env parameter is templated with jinja.
- You can use Jinja templating with every parameter that is marked as “templated” in the documentation
- Template substitution occurs just before the pre_execute function of your operator is called.
- You can also use Jinja templating with nested fields
- fields registered in template_fields property will be submitted to template substitution
- The template_fields property can equally be a class variable or an instance variable.
class MyDataReader: template_fields: Sequence[str] = ("path",) def __init__(self, my_path): self.path = my_path # [additional code here...] t = PythonOperator( task_id="transform_data", python_callable=transform_data, op_args=[MyDataReader("/tmp/{{ ds }}/my_file")], dag=dag, )2. Xcoms
Tasks talk to each other
- An XCom is identified by a key (essentially its name), as well as the task_id and dag_id
- XComs are explicitly “pushed” and “pulled” to/from their storage using the xcom_push and xcom_pull methods on Task Instances.
# Pulls the return_value XCOM from "pushing_task" value = task_instance.xcom_pull(task_ids='pushing_task')3. Dags
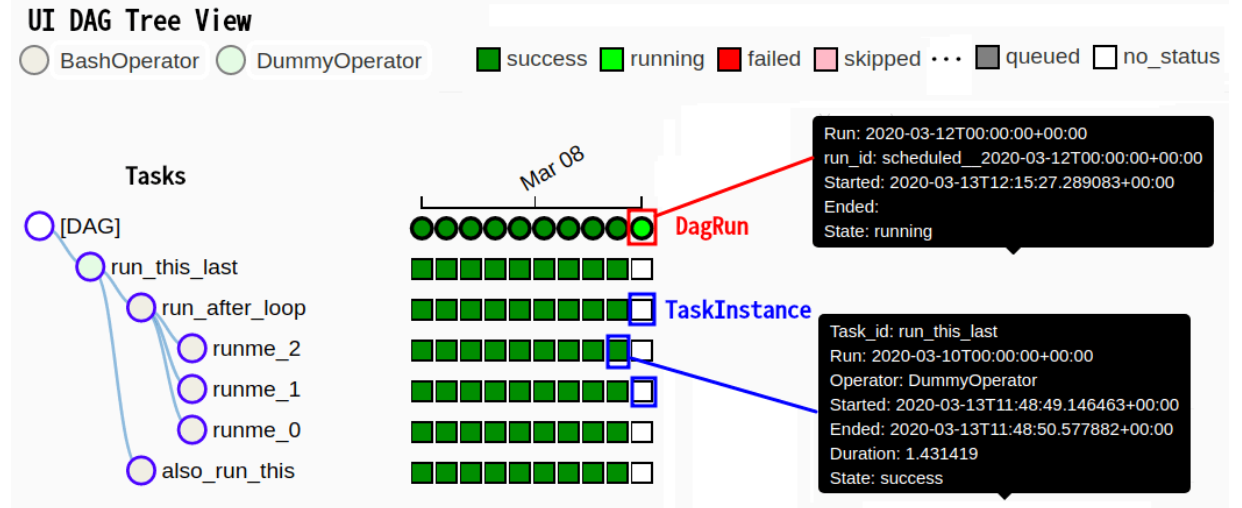
Dag status info
- Dagrun = Dag스케줄러(or Trigger)가 DAG의 execution_date(실행시간)를 정의하고 DagRun이 시간에 맞게 생성된다.
- Taskintance = 하나의 DagRun과 연관된 tasks 즉, 스케줄이 정의된 task를 TaskInstance라고 한다.
- execution_date = 스케줄링 된 실행시간을 의미
- start_date = 실제 dagrun이 실행된 시간을 의미
4. Executor
1. SequentialExector (default)- task 순차 처리 / SQLite3를 backend로 설정 / TEST로 사용 권장
2. LocalExecutor- task 병렬 처리 가능 / MySQL이나 PostgreSQL을 backend로 설정 / task마다 subprocess를 생성
3. CeleryExecutor- task를 여러 서버(node)에 분산 처리 가능 (cluster) / Celery backend (RabbitMQ, Redis, …) 설정이 필요
4. DaskExecutor- Celery와 같은 역할이지만 Dask로 처리
5. KubernetesExecutor- Kubernetes로 cluster 자원을 효율적으로 관리 가능
'개발 > Airflow' 카테고리의 다른 글
[Airflow] - Commands (0) 2022.08.03 [Airflow] - what is Airflow (0) 2022.07.30 [Airflow] - 7. Operator & Xcoms (0) 2022.07.20 [Airflow] - 6. Connect Postgresql (0) 2022.07.19 [Airflow] - 5.Postgresql 설치 및 DB setting (0) 2022.07.13